The Vendure Job Queue
What is a job queue?
Vendure uses a job queue to handle the processing of certain tasks which are typically too slow to run in the normal request-response cycle. A normal request-response looks like this:
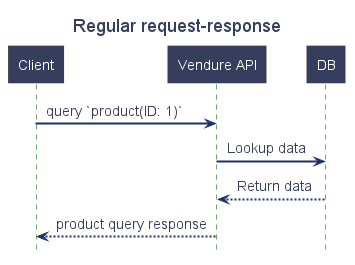
In the normal request-response, all intermediate tasks (looking up data in the database, performing business logic etc.) occur before the response can be returned. For most operations this is fine, since those intermediate tasks are very fast.
Some operations however will need to perform much longer-running tasks. For example, updating the search index on thousands of products could take up to a minute or more. In this case, we certainly don’t want to delay the reponse until that processing has completed. That’s where a job queue comes in:
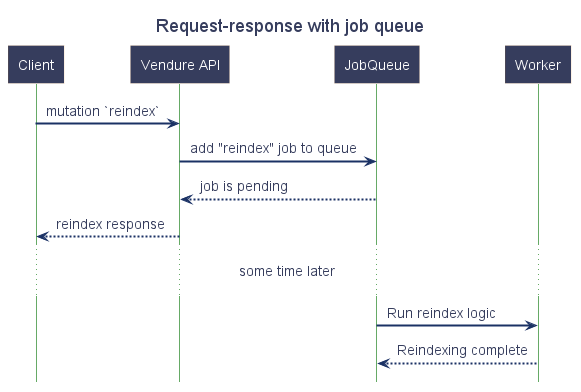
What does Vendure use the job queue for?
By default, Vendure uses the job queue for the following tasks:
- Re-building the search index
- Updating the search index when changes are made to Products, ProductVariants, Assets etc.
- Updating the contents of Collections
- Sending transactional emails
How does the Job Queue work?
This diagram illustrates the job queue mechanism:
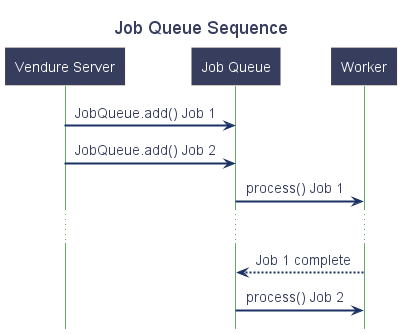
The server adds jobs to the queue. The worker then picks up these jobs from the queue and processes them in sequence, one by one (it is possible to increase job queue throughput by running multiple workers).
JobQueueStrategy
The actual queue part is defined by the configured JobQueueStrategy.
If no strategy is defined, Vendure uses an in-memory store of the contents of each queue. While this has the advantage of requiring no external dependencies, it is not suitable for production because when the server is stopped, the entire queue will be lost and any pending jobs will never be processed. Moreover, it cannot be used when running the worker as a separate process.
A better alternative is to use the DefaultJobQueuePlugin (which will be used in a standard @vendure/create installation), which configures Vendure to use the SqlJobQueueStrategy. This strategy uses the database as a queue, and means that even if the Vendure server stops, pending jobs will be persisted and upon re-start, they will be processed.
It is also possible to implement your own JobQueueStrategy to take advantage of other technologies. Examples include RabbitMQ, Google Cloud Pub Sub & Amazon SQS. It may make sense to implement a custom strategy based on one of these if the default database-based approach does not meet your performance requirements.
Job Queue Performance
It is common for larger Vendure projects to define multiple custom job queues, When using the DefaultJobQueuePlugin with many queues, performance may be impacted. This is because the SqlJobQueueStrategy uses polling to check for new jobs in the database. Each queue will (by default) query the database every 200ms. So if there are 10 queues, this will result in a constant 50 queries/second.
In this case it is recommended to try the BullMQJobQueuePlugin, which uses an efficient push-based strategy built on Redis.
Using Job Queues in a plugin
If you create a Vendure plugin which involves some long-running tasks, you can also make use of the job queue. See the JobQueue plugin example for a detailed annotated example.
A real example of this can be seen in the EmailPlugin source

